Introduction
Millions of people globally suffer from the significant issue of addiction to drugs, alcohol, and other harmful substances. The consequences of such habits include severe physical effects on one’s health, psychological impacts, and adverse social outcomes. This makes it vital for researchers to comprehend substance abuse, not through a narrow lens but instead recognize its long-term implications for collective well-being. Substance misuse could be influenced by several factors, including peer influence or pressure and economic circumstances leading individuals down this path over time. Additionally, mental issues arising after particular traumatic events can make an individual vulnerable to substance abuse.
Overall, any individual in a given population may feel such pressures more than others because everyone is unique. Often those addicted face numerous challenges, such as interpersonal problems alongside legal and financial constraints can directly associate these challenges with why they started abusing substances. Despite how devastating substance abuse can become to an individual, there is only hope unless the addiction is left unchecked. An individual can easily overcome the persistent substance abuse stigmatization with regular medical attention and counseling sessions tailored to address the underlying physical and mental conditions. This should also be supplemented by support networks where understanding staff helps guide clients psychologically and spiritually toward recovery.
Substance abuse prevention requires promoting a healthy lifestyle, educating people about the risks of substance abuse, and dealing with underlying issues that may trigger addiction. The UK’s youth are especially prone to substance abuse, which can have severe long-term implications. Young people’s substance addiction is an intense issue in underprivileged places like London’s Tower Hamlets, emphasizing the need for research that might help understand the underlying causal factors and develop effective intervention and preventive strategies. Developing strategies that can support young people in Tower Hamlets in leading healthy and prosperous lives is the ultimate goal of this study. An extensive scientific study using evidence-supported techniques will be implemented to collect research data. Ultimately, a population can live in a healthier, more encouraging environment if the members of the community and stakeholders work together to eliminate substance abuse in their region.
Data on the Selected Health Issue
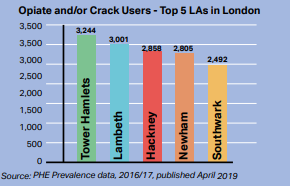
Several studies and research have been conducted to gather knowledge about the socio-demographic and epidemiological factors of substance use by various bodies, including community organizations, health professionals, and local government officials. Tower Hamlets district within London has a significant amount of information regarding substance abuse among children and young adults available locally (Tower Hamlets, 2019, p.1). Results from investigations into adolescent drug consumption rates as part of JSNA indicate that this borough has one of London’s highest percentages for illegal drug usage amongst its youth population. According to Figure 2 (Tower Hamlets, 2019, p.10), when compared with other areas in London, Tower Hamlets stands out with having the most significant estimation of users aged on crack cocaine or opioids, which leads us to understand how big the issue is posed by substance dependence specifically in the region.
The Joint Strategic Needs Assessment (JSNA) in Tower Hamlets (JSNA, 2016, p. 6) is an evidence-based and data-driven research document that outlines the drug use habits of children and young adults in the region. The study also reveals that among these substances, alcohol abuse ranks highest for this demographic living within Borough limits. The study further expounds on socio-demographic trends regarding substances like narcotics, marijuana, or amphetamines prescribed to treat ADHD symptoms effectively (Tower Hamlets, 2019, p. 10). Such research requires careful analysis of hard-to-interpret statistics found throughout sections dedicated to analyzing various aspects surrounding substance addiction experienced by today’s youth population residing in Tower Hamlets based on prosperity levels.
It was also noted how lower-income housing residents were more prone to having regular drug access than their more affluent peers. Other markers such as ethnicity or race and minority identification were identified as factors that increased the likelihood one might turn to substance abuse (Di Forti et al., 2019, p. 427). The survey also reveals that young people who are not in school or otherwise enrolled in education, employment, or training (NEET) are more likely to abuse drugs. Finally, the study discusses surprising figures shown through comparisons between Tower Hamlets’ death tolls due to substance abuse, as demonstrated in Figure 1 (Tower Hamlets, 2019, p. 10). This data was compared to country-wide averages taken directly from England government statistical supplies, revealing noticeable significant differences.
Several local neighborhood organizations have produced substance abuse data and information in the borough. These include Tower Hamlets Drugs and Alcohol Action Team (DAT), Drug Rehabilitation Requirement (DRR), and Alcohol Treatment Requirement (ATR). The DAT regularly conducts surveys and needs analyses to gauge the level of substance abuse in the region and to pinpoint the needs of young people battling addiction. Data from the DAT offer critical new understandings of abused substances, usage patterns, and causes of young people’s drug and alcohol use.
These statistics illustrate that substance abuse among younger people in the London area of Tower Hamlets is a severe public health concern that requires a timely response. Particularly among young people from underprivileged families and members of racial and ethnic minorities, underlying social and economic issues require attention (Di Forti et al., 2019, p. 427). The subsequent parts delve into greater depth regarding the health problem of substance abuse as we examine its causes, effects, and proposed solutions.
Background
In Tower Hamlets, there is a challenge with young people and children abusing illegal substances. The demographic composition and location are vital contributors to this health issue. Being a diversified borough inhabited by many youths and overall high population density, Tower Hamlets’ demography makes it more likely that the people will be at risk for substance abuse in Tower Hamlets (Di Forti et al., 2019, p. 426). According to the JSNA study on Tower Hamlets, individuals aged between 0-19 comprise a higher percentage than average given nationally (JSNA, 2016 p11). Moreover, research indicates that ethnic minorities have more excellent representation here compared to other areas, along with increased poverty levels which increase risks associated with drug use among residents.
It cannot be denied that the region of Tower Hamlets experiences the long-term effects of poverty, unemployment, and social isolation. However, these issues can breed feelings of hopelessness among young individuals who may seek refuge in drugs or alcohol to cope with their problems (Watt, 2021). According to JSNA’s survey on Tower Hamlets, evidence suggests that drug use or alcohol consumption is more prevalent among underprivileged families from ethnic minority backgrounds rather than affluent ones (JSNA, 2016, p.16). This report also emphasizes how substance abuse tends toward youths not enrolled in school or receiving training programs. This trend also resonates well since many juveniles are prone to dropping out early without seeking an education past secondary level schooling (Spencer et al., 2021, p.235). Thus, these factors become pivotal when understanding why substance abuse exists within young populations. Primarily mental illnesses are one such consequence that can arise due to poor economic conditions caused by societal pressures induced through marginalization (Spencer et al., 2021, p.235). The gathering data will result in careful analysis regarding various elements contributing significantly toward developing addiction amongst those affected residents living throughout targeted areas around Tower Hamlet.
Discussion of the Problem
The exploration of substance abuse among youngsters and adolescents in Tower Hamlets has been analyzed using various theoretical frameworks and theories from the social sciences. One such analysis is through the observational learning theory, which can be utilized to understand how peer pressure and communal expectations impact drug addiction among youth. The concept suggests that people develop their behaviors by imitating others, especially peers and role models (Sondhi et al., 2021, p. 90). Young individuals will likely replicate similar actions if they observe substance use within their friend circles or on social media platforms (Fardghassemi & Joffe, 2021,p.66). Children make up a large part of the London Borough Tower Hamlets’ population, increasing their chances of being exposed to substance abuse. Another theory, social identity, further reinforces this analysis, suggesting that one’s self-image mainly comes from interaction with peer groups and social networks. Consequently, interventions to develop healthy group dynamics and establish alternate opportunities for connection may effectively lower adolescent substance addiction rates.
The theory of social determinants of health can be applied to analyze why socio-economic status affects drug abuse among young people living in Tower Hamlets. This concept highlights how significant societal, financial, and environmental factors impact the overall well-being of an individual, especially regarding substance abuse. The presence of inequality within society results in elevated stress levels that eventually compel youths from this region towards substance abuse. To cope with poverty constraints or difficulties at home, young individuals seek refuge through harmful activities like drugs, hence a need for rehabilitation (Di Forti et al., 2019, p. 427). To compensate for unemployment, people may also resort to illegal means such as selling illicit drugs, which eventually develop adverse effects on their community’s welfare while increasing the risk of substance abuse by young people. The sociology concepts approach issues holistically by ensuring that every level participates equally (Sondhi et al., 2021, p. 90). In this case, quality life improvement measures should be taken hand-in-hand with enhanced public resources and diversifying income sources. All these efforts should prevent substance abuse amongst younger residents residing hereabouts via dexterously managing their everyday challenges while promoting positive coping mechanisms instead.
Studies on substance addiction among young people in Tower Hamlets can better be understood using social science theories and concepts. They can advise on creating effective interventions to address this issue. By implementing a multifaceted strategy that takes into account the individual, social, and environmental factors that contribute to substance abuse, stakeholders in Tower Hamlets intervention programs can work to reduce the prevalence of this problem and improve the health and well-being of young people in the borough.
Factors Leading to Substance Abuse
There are various reasons why children and young individuals in Tower Hamlets succumb to drug addiction. Consequently, the catalysts for their substance abuse are intricate. As per the social ecology theory, various factors such as ease of access to drugs and alcohol, environmental influence, and beliefs encircling substance use come into play in the heightened substance abuse among young individuals and children in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets (Xuan et al., 2021, p. 223). This signifies that challenging physical surroundings’ impact and societal norms could decrease narcotic intake rates amongst youngsters residing within Tower Hamlets region.
Most factors can be categorized as personal, societal, or environmental factors. Personal factors involve genetics, mental illnesses, and individual circumstances like stress, trauma, and a family history of substance abuse. Strained teenagers in Tower Hamlets are more likely to abuse alcohol and other drugs as a coping strategy for peer pressure, family conflicts, or academic tensions (Annan et al., 2022, p. 2200). Children who experience traumatic childhood experiences such as abuse, neglect, or parental divorce are also prone to abuse substances or alcohol as a means of coping. The likelihood that a child or young person would engage in substance abuse may also be increased if they grow up in a home where alcohol or substance abuse is prevalent.
Social elements that maintain significance in the London Borough of Tower Hamlet’s circumstance encompass peer pressure, cultural influences, and social standards. If young person highly prioritizes their desire to fit in with their peers, they may become more likely to participate in substance abuse which can lead to conformity (Annan et al., 2022, p.2200). Given this, children or adolescents may also be subject to pressures from their social circle, compelling them towards drug use for approval purposes. At the same time, cultural and societal beliefs around substances may affect the attitudes younger individuals may hold regarding substance abuse (Sondhi et al., 2021, p.90). Accessibility, as well as the availability of drugs and alcohol, are environmental factors that influence these decisions, coupled with socio-economic issues like unemployment, social inequality, and poverty. Despite its worsening effect on pre-existent difficulties, substance abuse is prevalent among youths from underprivileged backgrounds (Watt,2021). The diverse nature and the high deprivation levels characteristic within Tower Hamlets arguably determine an increased prevalence rate among marginalized groups. Young people from marginalized groups constitute a more significant proportion of the population in Tower Hamlets, where they could encounter more challenges finding the support and resources they require (Xuan et al., 2021, p. 224). Furthermore, due to the borough’s high population and easy substance access, young individuals may find it easier to access and engage in substance abuse.
Implications of Substance Abuse
Abuse of dangerous substances among the underage can significantly impact community and family life, as well as the safety of the general public domain. Substance abuse has also been linked to poor academic outcomes for young individuals (Spencer et al., 2021, p.230). Moreover, it is more likely that youths who make a habit out of substance abuse may become involved in illegal activities such as theft or violence, which could result in their eventual involvement within justice institutions.
Abusing substances could lead to several unfavorable outcomes for youths in Tower Hamlets. Based on research, the abuse of substances may cause significant medical and societal consequences like addiction and increased criminal behavior, as well as psychological effects such as depression and anxiety disorders (Spencer et al., 2021, p.230). A report conducted by Public Health England revealed that individuals under 18 years from Tower Hamlets had a high rate of admissions into hospitals, standing at 53.8 cases that specifically related to substance abuse when compared with a national average rate of 23.5 cases per every one hundred thousand people in the year 2018. Furthermore, there was also recorded an admission rate relating to substance abuse-related mental health issues, which stood at 38 .6 per every one hundred thousand individuals living within this London borough, while nationally noted only 14 .2 rate hospitalizations among similar groupings.
The implications of drug misuse can expand past the individual and onto families and society. Adolescents who engage in substance abuse may encounter societal rejection, dysfunctional relationships, as well as family disputes that could negatively affect their psychological state and overall welfare (Fardghassemi & Joffe, 2021: 66). The actions related to drugs raise criminal activities, particularly those linked with narcotics which poses a risk for Tower Hamlets’ security and its general wellness condition. Additionally, illicit substance abuse has substantial monetary consequences, such as decreased work efficiency levels or loss of productivity costs, medical expenses, and legal fees. According to estimations by the government within Tower Hamlets, damage caused solely due to alcohol is predicted annually beyond £60 million, thus emphasizing negative financial implications stemming from addiction on this region’s economy.
Prevention, early intervention, treatment, and support are critical to tackling substance abuse in Tower Hamlets. This includes encouraging healthy habits, educating individuals about the dangers and consequences of substance abuse, and addressing the root causes that lead to addiction (Hadland et al., 2021, p. 205). Early intervention and therapy can also prevent substance abuse from becoming an addiction. Community-based initiatives that prioritize building solid relationships and supporting young people and families impacted by substance abuse can help alleviate its harmful effects on the community. By collaborating, stakeholders in Tower Hamlets can lower the prevalence and impact of substance abuse, improve public health and well-being, and ensure a safer and happier community for everyone.
Critique of Existing Interventions to the Problem
The London Borough of Tower Hamlets has taken various actions to tackle substance abuse in minors. The measures were formulated by various groups that included officials from the locality, experts on healthcare, and community associations. A prime example is the collaboration between Compass Safe East and DAT (Drugs & Alcohol Action Team) which make up significant steps toward combating drug addiction among young individuals within this region. These strategic programs have various initiatives, from one-on-one sessions tailored to specific needs, counseling directed at families, and group events to build collective involvement (Hadland et al., 2021). To further advance their goal, they employ multidisciplinary approaches, where social work specialists teaming up with mental health care providers help streamline vital assistance targeted specifically towards rehabilitating the youth caught up in dependency-related trauma or issues faced while residing in Tower Hamlets.
The initiatives developed in Tower Hamlets reflect a successful collaboration between the local governance and healthcare sectors. Collaborative services also exist with joint efforts from authorities through Integrated Young People’s Substance Abuse and Mental Health Service to deliver comprehensive care to young people blended into other government provisions such as education or youth programs. Nevertheless, Tower Hamlets struggle persistently control juvenile substance abuse despite the significant input from public officials and stakeholders (Silverstein et al., 2021, p196). The primary obstacle to these interventions is inadequate funding, which means that the initiatives cannot effectively cater to the increasing needs for addiction in Tower Hamlets. In addition, empowering families and the young beneficiaries themselves requires a more sophisticated approach to drug dependency issues, which should be made available on demand at all times of need without hindrance whatsoever. This step will help avoid future relapse while promoting early intervention, hence preventing increased substance misuse levels in Tower Hamlets.
Proposed intervention to the problem
Addressing the public health issue of substance abuse among young individuals in Tower Hamlets, London, requires a multifaceted approach considering various factors. To effectively combat this problem, it is crucial to implement multiple strategies and interventions geared towards empowering youth and promoting beneficial community health practices (Hagell, 2021). The Social Learning Theory holds significance in emphasizing how social influence plays an essential role in shaping people’s behaviors (Xuan et al., 2021). Thus intervention programs must focus on changing the environment surrounding young people by guiding them through encouraging healthy lifestyles while giving youths autonomy over their decisions. Partnerships with educational institutions and local organizations dedicated to improving communities’ welfare, such as youth centers, should focus on targeting diversified populations within boroughs to bring positive change.
The proposed plan aims to tackle substance abuse among young people in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets through a well-rounded strategy. The proposed program includes campaigns that inform and educate, treatment programs and services, as well as regulations for enforcement. This initiative promotes healthy habits and raises awareness about the dangers of substance abuse among the public (Brown & Wincup, 2020). Educating younger individuals is essential by conducting interactive workshops hosted by peers or community events designed around up-to-date information regarding the implications of substance abuse (Xuan et al., 2021). Lastly, an extensive social marketing campaign will be implemented to encourage balanced lifestyles while educating on the negative impacts caused by abusing substances. This approach should increase understanding within society’s population over time.
The program will involve therapy sessions to aid adolescents who engage in substance abuse, conquer their addiction and prevent relapse (Levy and Botticelli, 2021, p. 263). Youths struggling with drug or alcohol dependency may benefit from the implemented interventions such as psychotherapy, rehabilitation treatment plans, and psychological services to tackle the root causes of substance abuse (Hadland et al., 2021, p.205). Individualized programs are intended to provide young people with the necessary assistance while addressing the underlying issues that lead them toward addictive behaviors. Essentially, we can help the youths tackle their substance abuse by providing a support system where they acquire essential strategies for recovery and maintenance alongside preventing future relapses (Xuan et al., 2021, p. 224). With counseling treatments and other forms of emotional well-being healthcare facilities readily available, youth experiencing these difficulties can get back on track to recovery (Hadlandet el.,2017). These provisions offer solutions that tackle the fundamental drivers behind illegal substance abuse, specifically amongst children and young people, while promoting overall health and wellness within society.
Implementing strict regulations and enforcement actions can help limit the availability of substances and alcohol among minors. Such objectives may be achieved by targeting those involved in producing, distributing, or selling these substances through effective law enforcement measures (Brown & Wincup 2020; p.12). Making it challenging to access illicit substances could discourage underage consumption, reducing incidences of substance abuse among young adults. A framework based on social determinants is suitable for addressing root causes leading to drug addiction issues within the Tower Hamlets youth community. The practical application highlights how environmental factors alongside social-economic aspects play a significant role when determining health outcomes, including but not limited to addictive behaviors like substance abuse.
Recommendations
Social science theories and research should drive practical approaches to stop substance abuse among children and young people in Tower Hamlets. Interventions should concentrate on fostering resilience and encouraging young people to adopt healthy behaviors at the individual level. This could entail making support services for substance abuse and mental health accessible and encouraging constructive peer interactions and healthy coping mechanisms (Hagell, 2021). Interventions at the interpersonal level should focus on how peer and family relationships affect young people’s perception of substance abuse (Harrington et al., 2020, p. 271). Parenting programs and other family-based interventions can also help to improve healthy family dynamics and lower the likelihood of substance abuse in Tower Hamlets. Peer-led initiatives, including peer mentoring programs, can also help promote positive social norms and decrease the impact of adverse peer pressure.
Interventions should focus on the social determinants of health that influence substance abuse among young people in Tower Hamlets at the community level. This could entail collaborating with nearby schools, youth groups, and community organizations to offer young people beneficial options like sports and arts activities. Interventions could also expand young people’s access to training, job, and educational opportunities in the borough (Harrington et al., 2020, p. 271). Interventions at the social level should target the structural causes of substance abuse among young people in Tower Hamlets. Advocating for laws and initiatives that advance social justice and lessen health disparities among different populations may fall under this category (Brown and Wincup, 2020, p. 12). Interventions should also emphasize the accessibility to affordable housing, healthcare, employment, and lowering poverty levels in the borough.
Conclusion
Tower Hamlets have had a significant issue with substance abuse among young people. This problem is exacerbated by the borough’s high levels of social exclusion, unemployment, and poverty, especially for marginalized minorities. Many youths in the region indulge in alcohol or drug abuse, highlighting the severe issue of substance abuse. Tackling such public health issues head-on requires decisive action that considers underlying societal factors while upholding support mechanisms for those who suffer from addiction. A comprehensive strategy must be put forth to aim toward the betterment of future generations that may be plagued with complex problems like these.
References
Annan, L.G., Gaoua, N., Mileva, K. and Borges, M., 2022. What makes young people get involved with street gangs in London? A study of the perceived risk factors. Journal of community psychology, 50(5), pp.2198-2213. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcop.22767
Brown, K. and Wincup, E., 2020. Producing the vulnerable subject in English drug policy. International Journal of Drug Policy, 80, p.102525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugpo.2019.07.020
Department of Health and Social Care (2016) Joint strategic needs assessment and joint health and well-being strategies explained., GOV.UK. GOV.UK. Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/joint-strategic-needs-assessment-and-joint-health-and-wellbeing-strategies-explained
Di Forti, M., Quattrone, D., Freeman, T.P., Tripoli, G., Gayer-Anderson, C., Quigley, H., Rodriguez, V., Jongsma, H.E., Ferraro, L., La Cascia, C. and La Barbera, D., 2019. The contribution of cannabis use to variation in the incidence of psychotic disorder across Europe (EU-GEI): a multicentre case-control study. The Lancet Psychiatry, 6(5), pp.427-436. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(19)30048-3
Fardghassemi, S. and Joffe, H., 2021. Young adults’ experience of loneliness in London’s most deprived areas. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, p.660791. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.66079
Hadland, S.E., Yule, A.M., Levy, S.J., Hallett, E., Silverstein, M. and Bagley, S.M., 2021. Evidence-based treatment of young adults with substance use disorders. Pediatrics, 147(Supplement 2), pp.S204-S214. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-023523D
Hagell, A., 2021. HEALTHSPOT: Implementing an innovative GP service for young people at Spotlight youth service in Tower Hamlets. https://www.northeastlondonhcp.nhs.uk/downloads/ourplans/Children/Spotlight/Healthspot%
20AYPH%20Evaluation%20FINAL%20060421.pdf
Harrington, R.A., Gray, M. and Jani, A., 2020. Digitally enabled social prescriptions: adaptive interventions to promote health in children and young people. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 113(7), pp.270-273. https://doi.org/10.1177/0141076819890548
Levy, S. and Botticelli, M., 2021. Moving to a medical model of substance use treatment of youth. Pediatrics, 147(Supplement 2), pp.S262-S264. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-023523J
London borough of tower hamlets (2018). Available at: https://democracy.towerhamlets.gov.uk/documents/s159058/6.1%20Refresh%20of%20TH%
20Substance%20Misuse%20Strategy%202020-2025.pdf
Silverstein, M., Hadland, S.E., Hallett, E. and Botticelli, M., 2021. Principles of care for young adults with substance use disorders. Pediatrics, 147(Supplement 2), pp.S195-S203. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-023523B
Sondhi, A., Leidi, A. and Gilbert, E., 2021. A Small Area Estimation Method for Investigating the Relationship between Public Perception of Drug Problems with Neighborhood Prognostics: Trends in London between 2012 and 2019. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(17), p.9016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18179016
Spencer, A.E., Valentine, S.E., Sikov, J., Yule, A.M., Hsu, H., Hallett, E., Xuan, Z., Silverstein, M. and Fortuna, L., 2021. Principles of care for young adults with co-occurring psychiatric and substance use disorders. Pediatrics, 147(Supplement 2), pp.229-239. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-023523F
Tower Hamlets Partnership Substance Misuse Strategy 2020-2025 (2019). Available at: https://democracy.towerhamlets.gov.uk/documents/s159059/6.1a%20Appendix%201
%20Refresh%20of%20Tower%20Hamlets%20Substance%20Misuse%20Strategy.pdf
Watt, P., 2021. The research boroughs and their estates. In Estate Regeneration and Its Discontents (pp. 89-124). Policy Press. https://doi.org/10.51952/9781447329213.ch004
Xuan, Z., Choi, J., Lobrutto, L., Cunningham, T., Castedo de Martell, S., Cance, J., Silverstein, M., Yule, A.M., Botticelli, M. and Holleran Steiker, L., 2021. Support services for young adults with substance use disorders. Pediatrics, 147(Supplement 2), pp.S220-S228. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-023523E
Appendices
Figure 1: The trend in deaths from drug misuse in Tower Hamlets
Source: Office for National Statistics (ONS)
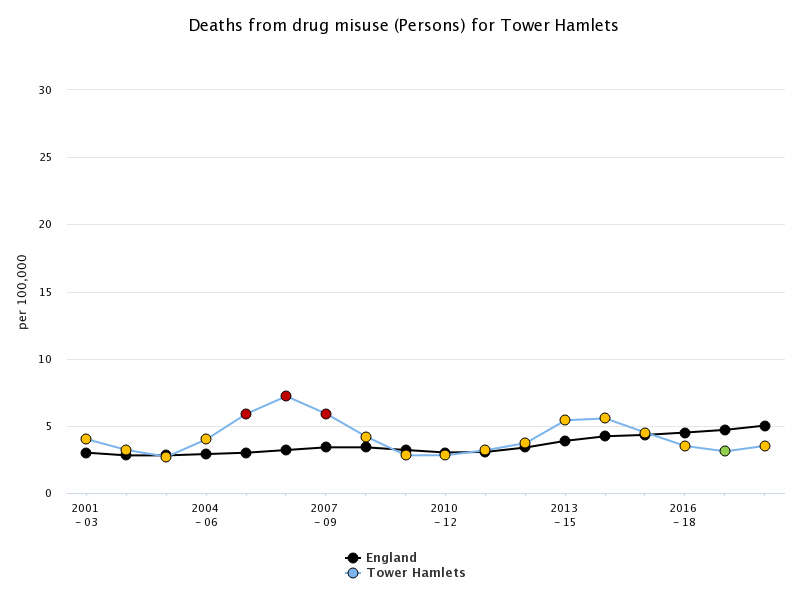
Figure 2: Trends showing the drug prevalence data in London (Opiate and/or crack)
Source: PHE Prevalence data, 2016/17, published April 2019
>